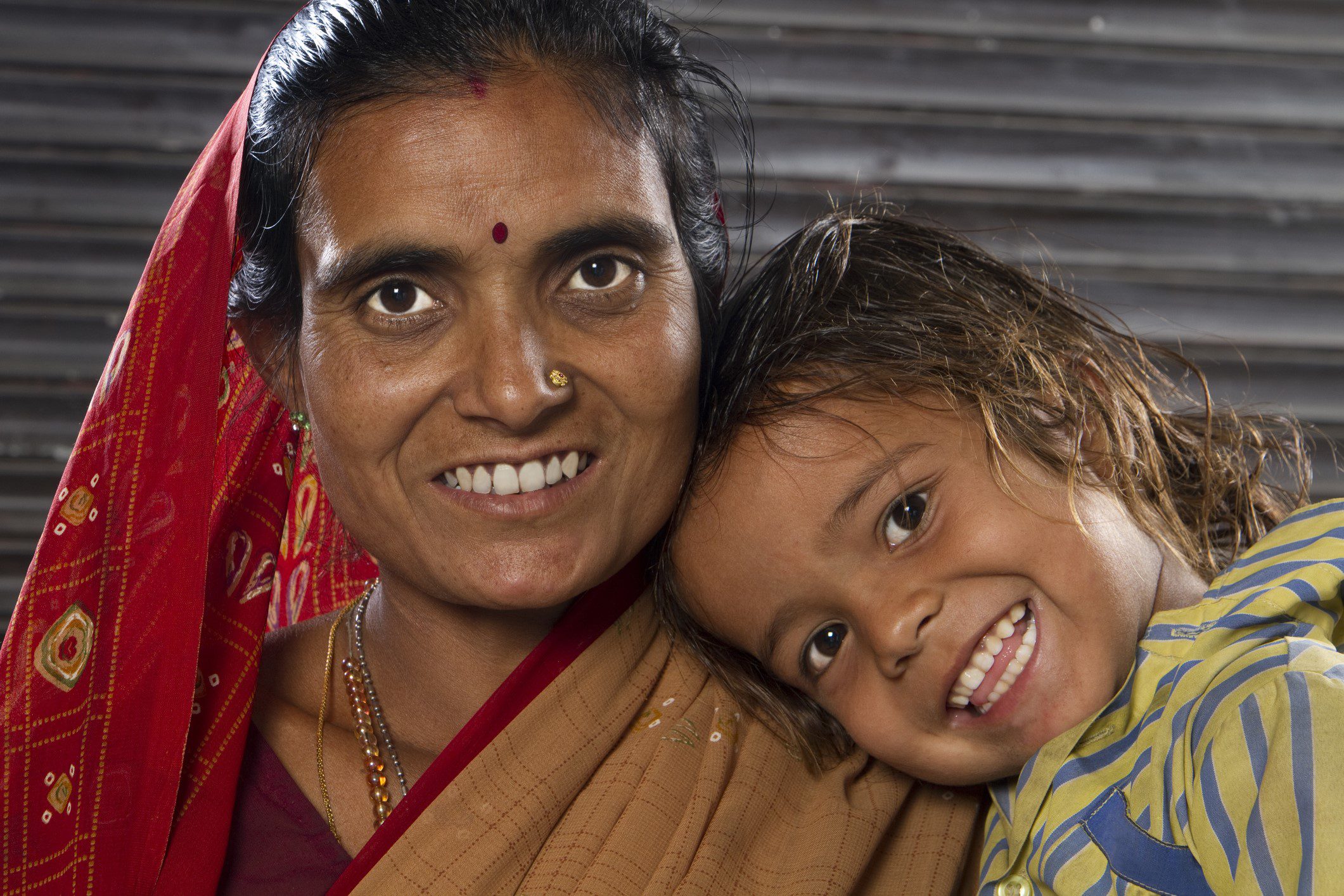
Access to Credit
Blended Finance

The need for blended finance in India
Blended finance (BF) is the strategic use of development finance from public and philanthropic sources to mobilise additional capital from the private sector towards greater, sustainable impact. Typically, grant funding is blended with other sources of capital such as debt or equity to maximize funding and social impact capacity.
Blended finance provides opportunities for transformation of the social impact space by working at the intersection of sarkaar, bazaar and samaaj. It uses a network mindset, bringing with it a set of partners, protocols and governance rules, to design interventions and amplify impact at-scale.
The Indian BF market stood at USD 1.30 billion in 2022. This represents 14.0% of the global BF market by value and is projected to reach USD 2.64 billion by 2027.
The Indian BF market has grown by 8x from USD 0.1 billion to USD 1.1 billion during the 13-year period from 2010-2022. This indicates a compound annual growth rate of (CAGR) of 18.8%, higher than the growth rate of the global BF market at 11.0%. It represented a cumulative market size of USD 5.6 billion during the 13-year period from 2010-2022, about 3.4% of the cumulative global market.
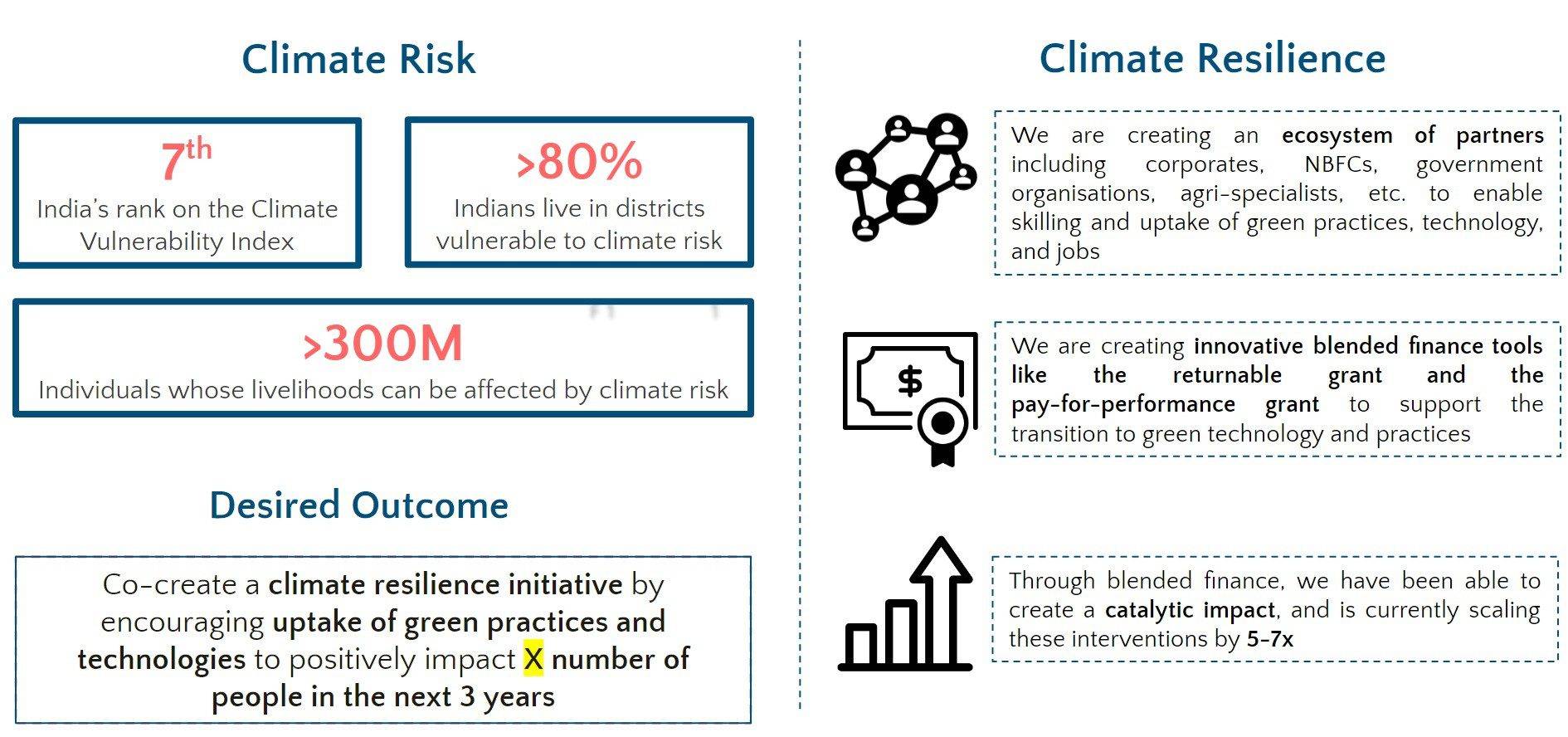
Challenges to generating livelihoods
welfare schemes
Participation Rate (FLFPR)
There is a massive credit gap of $530 billion in the MSME sector in India. Out of more than 64 million MSMEs, only 14% have access to credit.
47% of the debt demand is unaddressable as it comes from "enterprises which are not financially viable or prefer financing from informal sources.”
Only 6% of all MSMEs actively sell on e-commerce platforms. Owing to the informal nature of businesses, entering and navigating the market can be a daunting task. Limited market knowledge and resources exacerbate the challenges.
The Indian government spends over 7% of its GDP on welfare services. But there’s still a huge gap in the demand and supply, resulting in unspent funds.
India’s FLFPR is abysmally low at 23%, as compared to other emerging economies like Vietnam (~70%). while more women have a bank a/c now, with no gender gap, the number of women aged 15-49 who have money that they can decide how to use has grown very tepidly, from 44.6% to 51.2% between NFHS-3 IN 2005-06 and NFHS-5 IN 2019-21.
Challenges to generating livelihoods
welfare schemes
Participation Rate (FLFPR)
There is a massive credit gap of $530 billion in the MSME sector in India. Out of more than 64 million MSMEs, only 14% have access to credit.
47% of the debt demand is unaddressable as it comes from "enterprises which are not financially viable or prefer financing from informal sources.”
Only 6% of all MSMEs actively sell on e-commerce platforms. Owing to the informal nature of businesses, entering and navigating the market can be a daunting task. Limited market knowledge and resources exacerbate the challenges.
The Indian government spends over 7% of its GDP on welfare services. But there’s still a huge gap in the demand and supply, resulting in unspent funds.
India’s FLFPR is abysmally low at 23%, as compared to other emerging economies like Vietnam (~70%). while more women have a bank a/c now, with no gender gap, the number of women aged 15-49 who have money that they can decide how to use has grown very tepidly, from 44.6% to 51.2% between NFHS-3 IN 2005-06 and NFHS-5 IN 2019-21.
Challenges of the informal economy
Credit gap
Informal sources of finance
Lack of access to government welfare schemes
Low market linkages
Low Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR)

Credit gap
There is a massive credit gap of $530 billion in the MSME sector in India. Out of more than 64 million MSMEs, only 14% have access to credit.

Informal sources of finance
47% of the debt demand is unaddressable as it comes from "enterprises which are not financially viable or prefer financing from informal sources.”

Lack of access to government welfare schemes
The Indian government spends over 7% of its GDP on welfare services. But there’s still a huge gap in the demand and supply, resulting in unspent funds.

Low market linkages
Only 6% of all MSMEs actively sell on e-commerce platforms. Owing to the informal nature of businesses, entering and navigating the market can be a daunting task. Limited market knowledge and resources exacerbate the challenges.

Low Female Labour Force Participation Rate (FLFPR)
India’s FLFPR is abysmally low at 23%, as compared to other emerging economies like Vietnam (~70%). while more women have a bank a/c now, with no gender gap, the number of women aged 15-49 who have money that they can decide how to use has grown very tepidly, from 44.6% to 51.2% between NFHS-3 IN 2005-06 and NFHS-5 IN 2019-21.
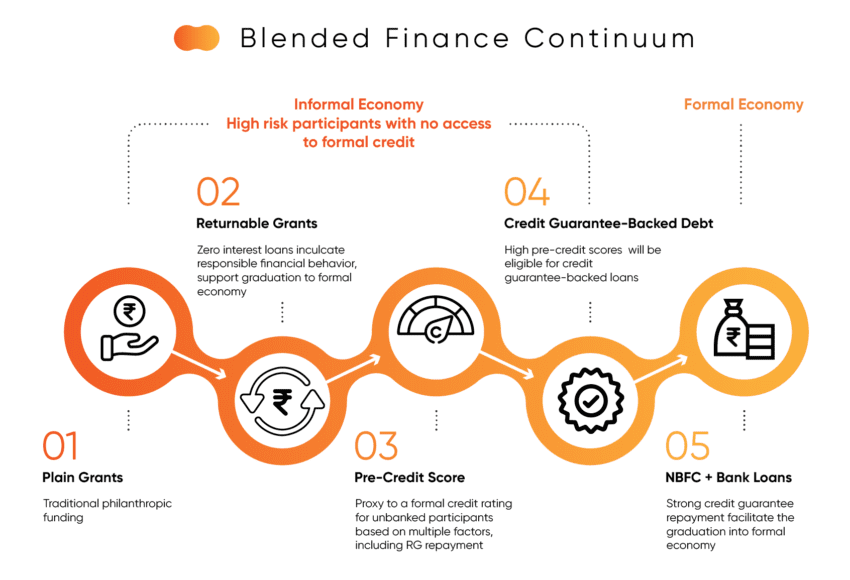
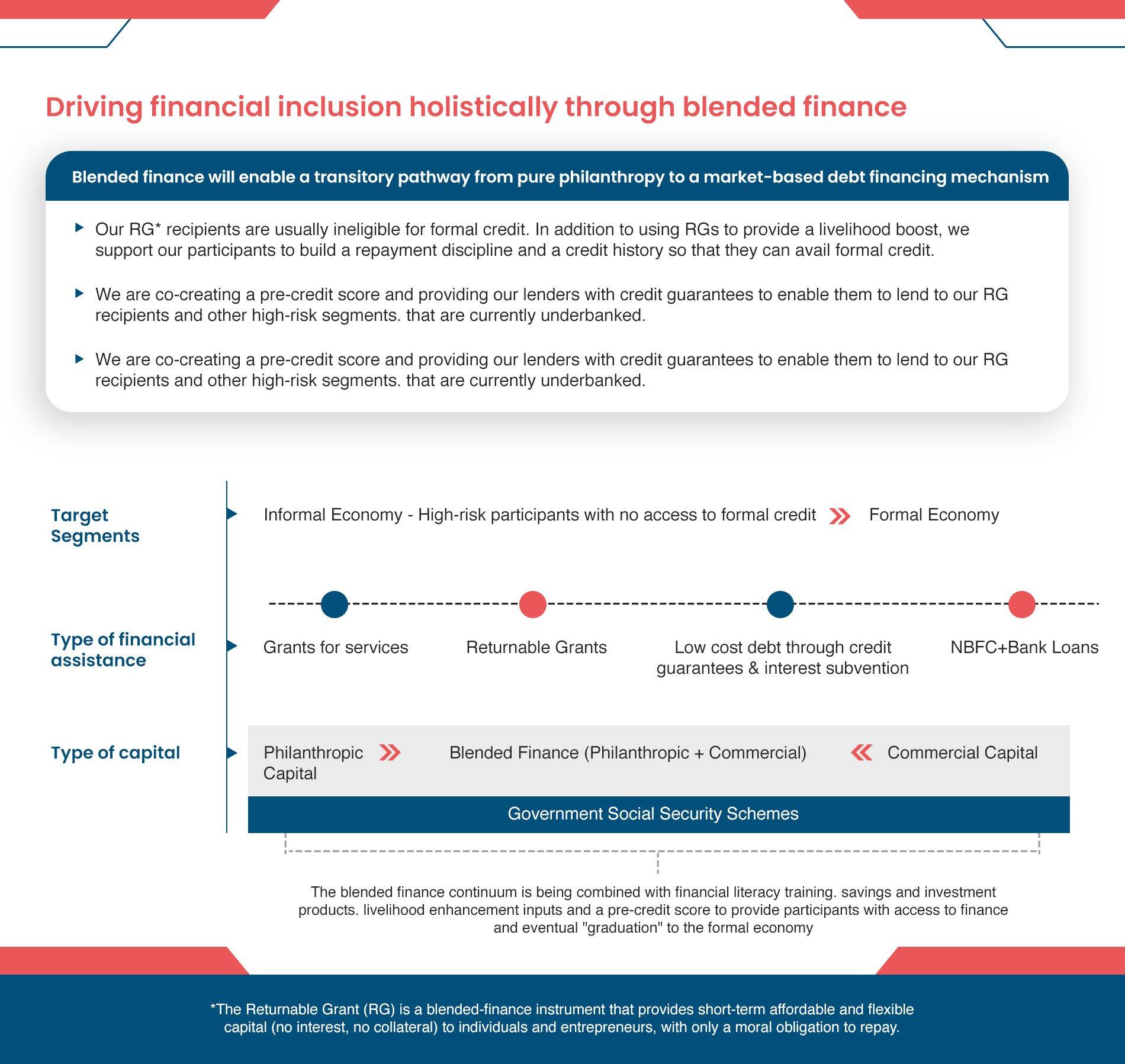
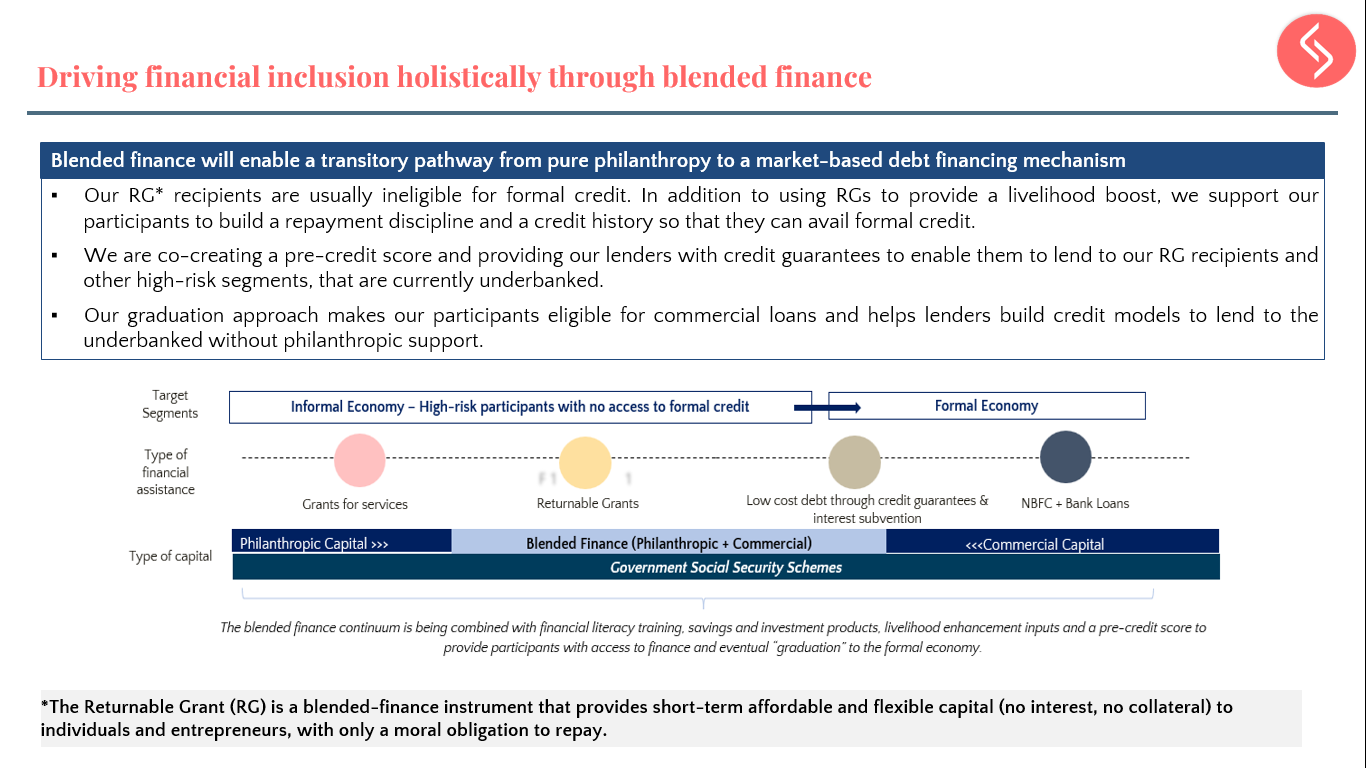
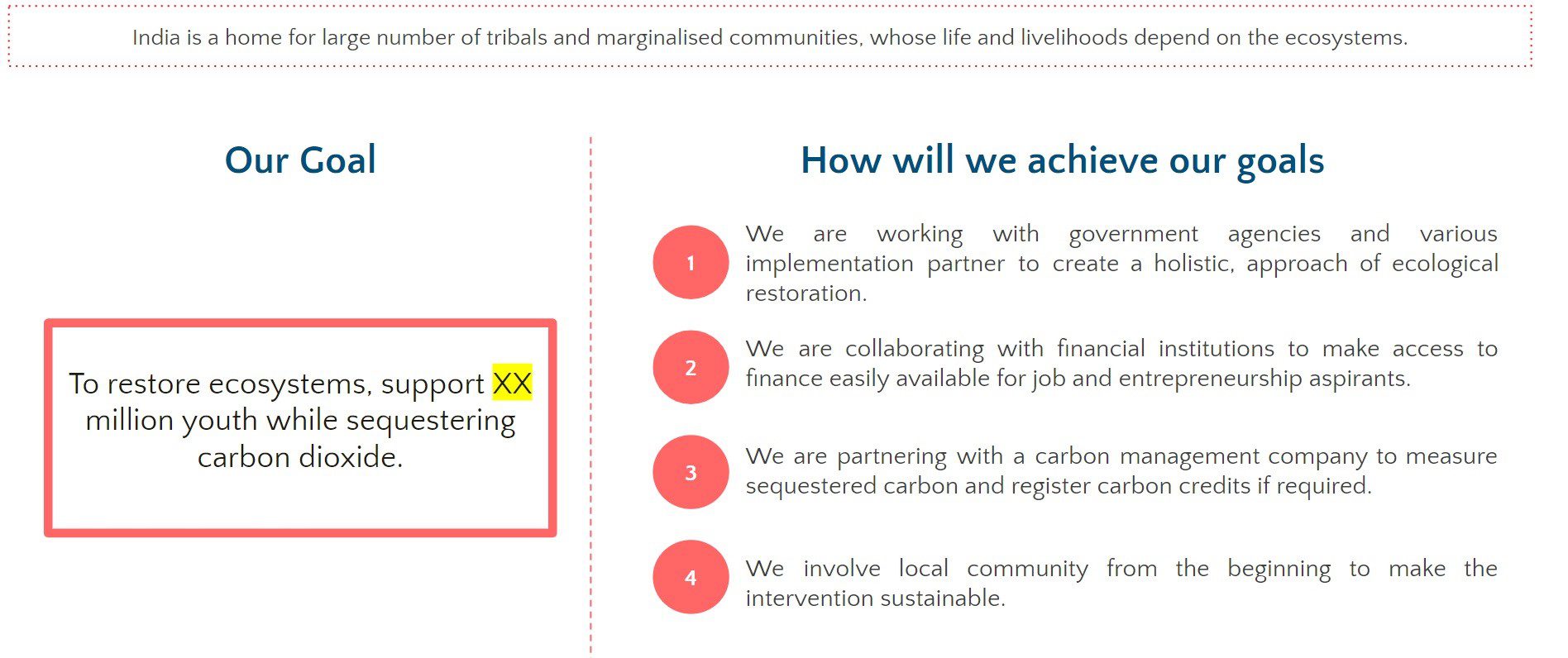
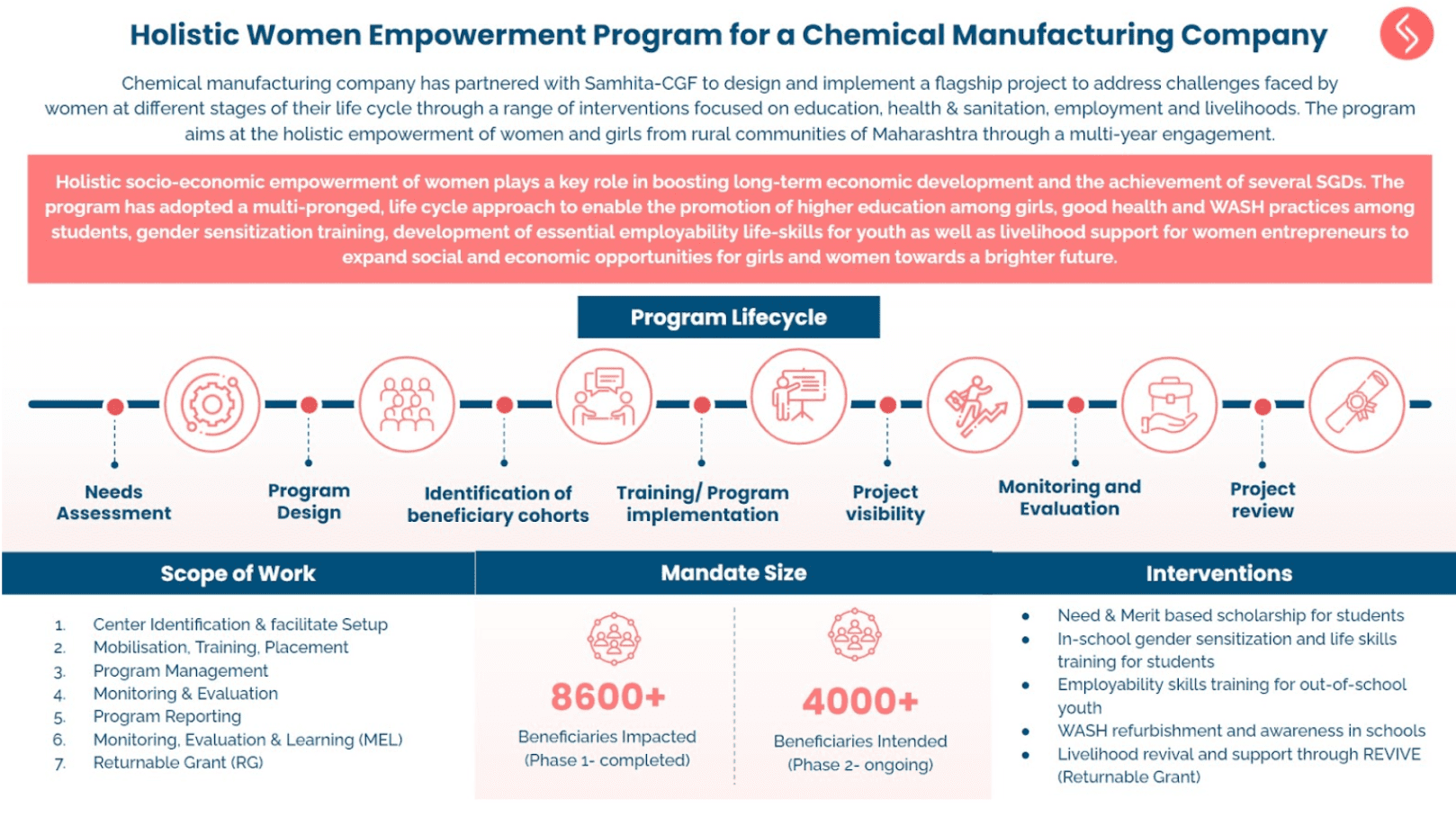
Samhita-CGF’s Blended Finance Continuum
Over 80% of our target segment of informal workers and entrepreneurs are either NTI, NTC, or New to Formal Credit (NTFC), and hence are not deemed to be creditworthy by formal lending institutions. NBFCs consider our target segment of informal workers and micro-entrepreneurs to be “high-risk” customers, and hence they are unable to “graduate” into the formal economy.
We aim to leverage our partner ecosystem to bridge this gap and help bring informal workers and micro-entrepreneurs, both new and existing, into the formal economy by co-creating financial inclusion and livelihood improvement programs to support NTI, NTC and NTFC segments.
The Graduation Approach
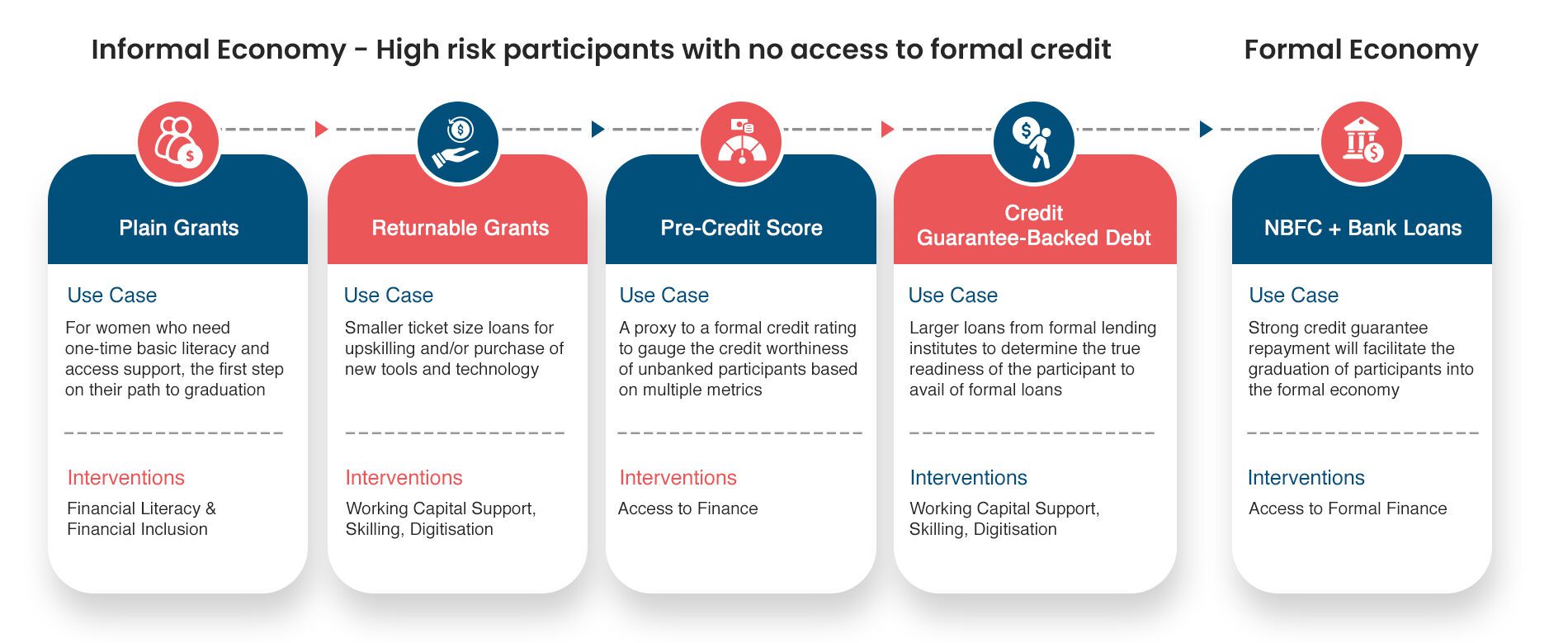
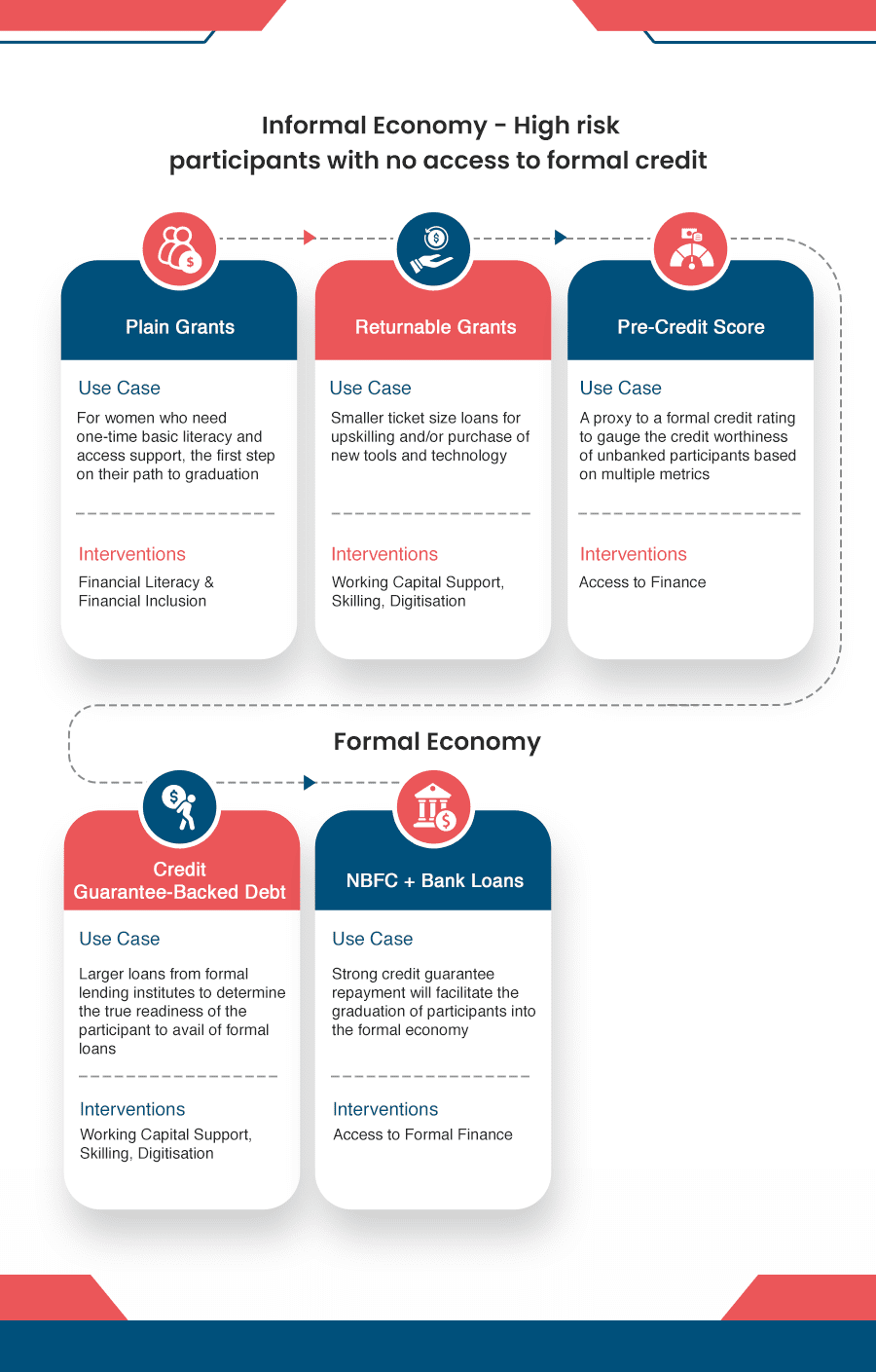
The power of Returnable Grants (RGs)

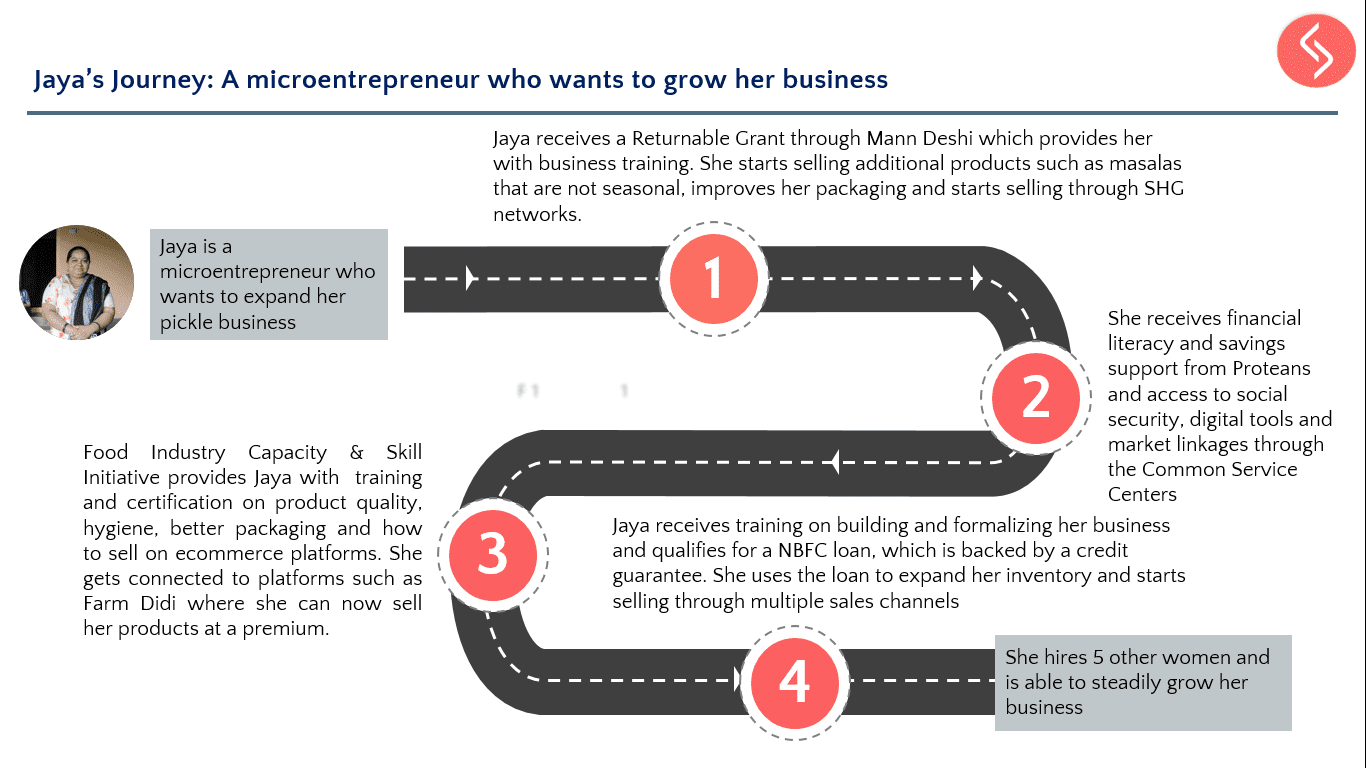
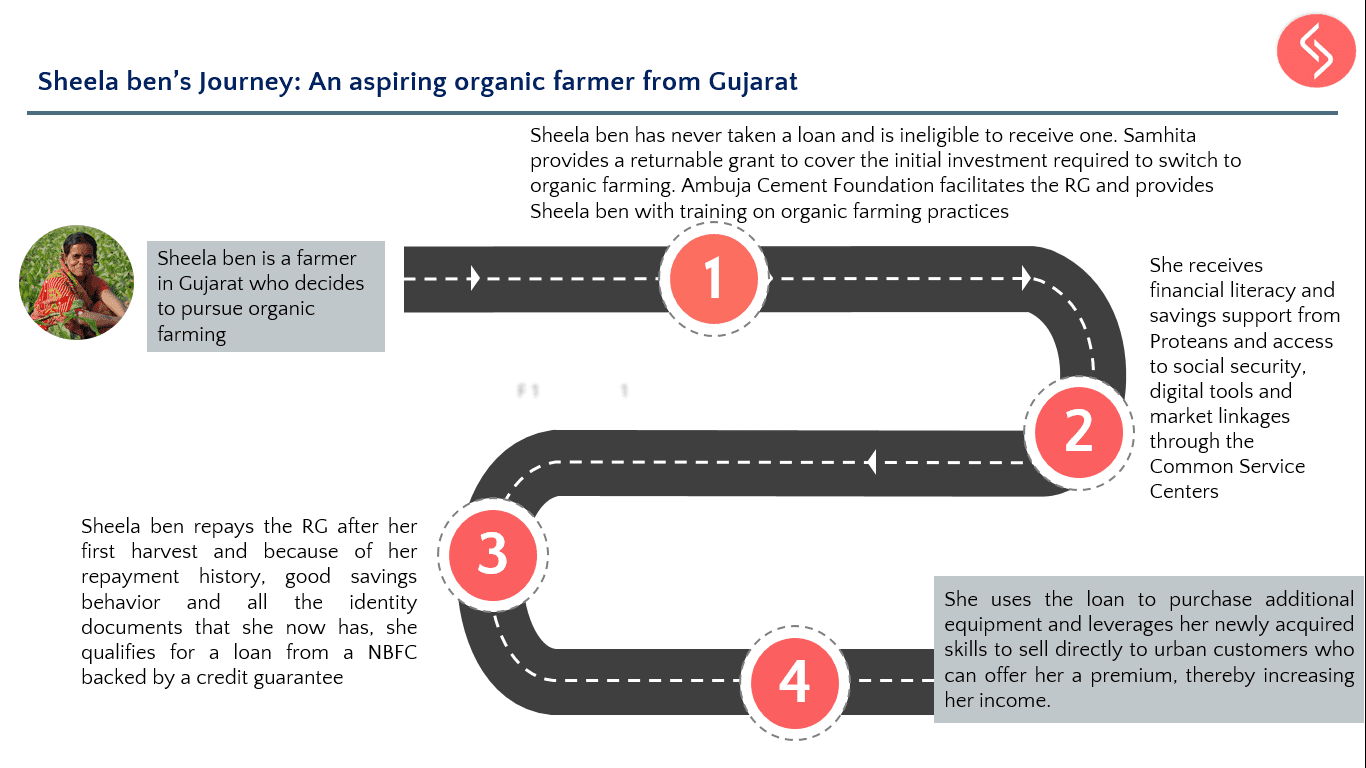
Samhita-CGF’s Returnable Grant (RG) is a zero interest, zero collateral loan with no legal obligation to repay, only a moral obligation used to address the capital gap and enable entrepreneurs, informal workers, and those aspiring to be a part of the workforce to increase their incomes. We have impacted the lives of +34,500 participants so far!

The power of Returnable Grants (RGs)
Samhita-CGF’s Returnable Grant (RG) is a zero interest, zero collateral loan with no legal obligation to repay, only a moral obligation used to address the capital gap and enable entrepreneurs, informal workers, and those aspiring to be a part of the workforce to increase their incomes. We have impacted the lives of +34,500 participants so far!
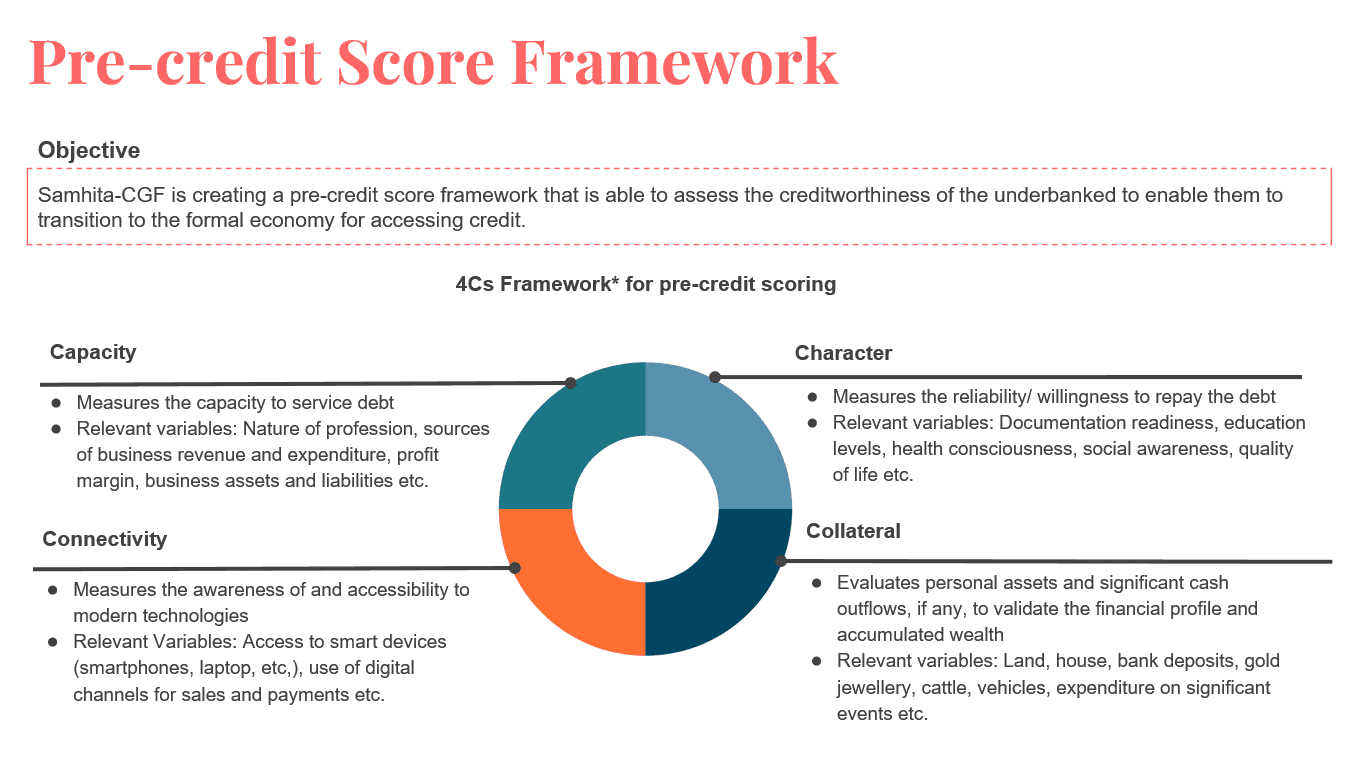
Pre-Credit Scores and Credit Guarantees - The next level
Pre-credit Score
Credit Guarantees
The Samhita-CGF Advantage
Shifting CSR Spend Discourse from Compliance to Catalyst
Our success with REVIVE makes us believe that Indian corporates are open to more innovative approaches in their CSR financing, including blended finance instruments, to expand the share of their operations and financing to more poorer states.
Local Expertise and Networks:
We have a deep understanding of the local context and strong networks within communities, CSRs and NGOs. This allows us to identify high-impact projects and effectively mobilize resources
Innovative Financing Models:
Samhita-CGF is known for pioneering innovative financing models that blend public and private resources in creative ways, ensuring maximum impact for every rupee invested.
Broad Spectrum of Financial Institutions:
We work closely with various financial institutions, including NBFCs and Banks, to create tailored financial solutions that support our blended finance initiatives.
Shifting CSR Spend Discourse from Compliance to Catalyst
Our success with REVIVE makes us believe that Indian corporates are open to more innovative approaches in their CSR financing, including blended finance instruments, to expand the share of their operations and financing to more poorer states.
Local Expertise and Networks:
We have a deep understanding of the local context and strong networks within communities, CSRs and NGOs. This allows us to identify high-impact projects and effectively mobilize resources
Innovative Financing Models:
Samhita-CGF is known for pioneering innovative financing models that blend public and private resources in creative ways, ensuring maximum impact for every rupee invested.
Broad Spectrum of Financial Institutions:
We work closely with various financial institutions, including NBFCs and Banks, to create tailored financial solutions that support our blended finance initiatives.
Diverse Partnerships and Collaborations:
We have established multiple partnerships and collaborations with a wide array of organizations, including Appreciate, Common Service Centers, USAID, MSDF, Microsoft, Google, S&P Global, Godrej, Mann Deshi, SEWA, Kotak, IndusInd, Yes Bank, SIDBI, UGro, Avanti Microfinance, and others. These alliances strengthen our ability to mobilize resources and implement impactful projects.
Rigorous Impact Assessment:
- We employ robust impact assessment methodologies to measure and report the outcomes of our blended finance initiatives. This accountability ensures transparency and demonstrates the tangible difference we're making.
- We have developed four specialized indices - the Income Index, Resilience Index, Economic Empowerment Index, and Women’s Economic Empowerment Index. These indices serve as powerful tools for precise impact assessment, providing invaluable insights into the effectiveness of our programs on an entrepreneur’s economic progression.
Diverse Partnerships and Collaborations:
We have established multiple partnerships and collaborations with a wide array of organizations, including Appreciate, Common Service Centers, USAID, MSDF, Microsoft, Google, S&P Global, Godrej, Mann Deshi, SEWA, Kotak, IndusInd, Yes Bank, SIDBI, UGro, Avanti Microfinance, and others. These alliances strengthen our ability to mobilize resources and implement impactful projects.
Rigorous Impact Assessment:
- We employ robust impact assessment methodologies to measure and report the outcomes of our blended finance initiatives. This accountability ensures transparency and demonstrates the tangible difference we're making.
- We have developed four specialized indices - the Income Index, Resilience Index, Economic Empowerment Index, and Women’s Economic Empowerment Index. These indices serve as powerful tools for precise impact assessment, providing invaluable insights into the effectiveness of our programs on an entrepreneur’s economic progression.
Compliance of Blended Finance instruments
Noshir Dadrawala, Chief Executive of the Centre for Advancement of Philanthropy, on the CSR and FCRA compliance of Returnable Grants and Credit Guarantees
Compliance of Blended Finance instruments
Noshir Dadrawala, Chief Executive of the Centre for Advancement of Philanthropy, on the CSR and FCRA compliance of Returnable Grants and Credit Guarantees
The Samhita-CGF advantage
and Networks
Financing Models
and Collaborations
Financial Institutions
Assessment
We have a deep understanding of the local context and strong networks within communities, CSRs and NGOs. This allows us to identify high-impact projects and effectively mobilize resources
Samhita-CGF is known for pioneering innovative financing models that blend public and private resources in creative ways, ensuring maximum impact for every rupee invested.
We have established multiple partnerships and collaborations with a wide array of organizations, including Appreciate, Common Service Centers, USAID, MSDF, Microsoft, Google, S&P Global, Godrej, Mann Deshi, SEWA, Kotak, IndusInd, Yes Bank, SIDBI, UGro, Avanti Microfinance, and others. These alliances strengthen our ability to mobilize resources and implement impactful projects.
We work closely with various financial institutions, including NBFCs and Banks, to create tailored financial solutions that support our blended finance initiatives.
- We employ robust impact assessment methodologies to measure and report the outcomes of our blended finance initiatives. This accountability ensures transparency and demonstrates the tangible difference we're making.
- We have developed four specialized indices - the Income Index, Resilience Index, Economic Empowerment Index, and Women’s Economic Empowerment Index. These indices serve as powerful tools for precise impact assessment, providing invaluable insights into the effectiveness of our programs on an entrepreneur’s economic progression.
Our success with REVIVE makes us believe that Indian corporates are open to more innovative approaches in their CSR financing, including blended finance instruments, to expand the share of their operations and financing to more poorer states.
The Samhita-CGF advantage
and Networks:
Financing Models
and Collaborations:
Financial Institutions:
Assessment:
We have a deep understanding of the local context and strong networks within communities, CSRs and NGOs. This allows us to identify high-impact projects and effectively mobilize resources
Samhita-CGF is known for pioneering innovative financing models that blend public and private resources in creative ways, ensuring maximum impact for every rupee invested.
We have established multiple partnerships and collaborations with a wide array of organizations, including Appreciate, Common Service Centers, USAID, MSDF, Microsoft, Google, S&P Global, Godrej, Mann Deshi, SEWA, Kotak, IndusInd, Yes Bank, SIDBI, UGro, Avanti Microfinance, and others. These alliances strengthen our ability to mobilize resources and implement impactful projects.
We work closely with various financial institutions, including NBFCs and Banks, to create tailored financial solutions that support our blended finance initiatives.
- We employ robust impact assessment methodologies to measure and report the outcomes of our blended finance initiatives. This accountability ensures transparency and demonstrates the tangible difference we're making.
- We have developed four specialized indices - the Income Index, Resilience Index, Economic Empowerment Index, and Women’s Economic Empowerment Index. These indices serve as powerful tools for precise impact assessment, providing invaluable insights into the effectiveness of our programs on an entrepreneur’s economic progression.
Our success with REVIVE makes us believe that Indian corporates are open to more innovative approaches in their CSR financing, including blended finance instruments, to expand the share of their operations and financing to more poorer states.
Alliances and Collaborations

REVIVE

Revive

Mera Gaon, Mera Pride

Women’s Health Alliance
REVIVE is a multi-intervention and multi-stakeholder livelihood accelerator that enables the economic recovery, resilience and growth of informal workers and microentrepreneurs.

Pragati Alliance
REVIVE is a multi-intervention and multi-stakeholder livelihood accelerator that enables the economic recovery, resilience and growth of informal workers and microentrepreneurs.
Latest News
- June 20, 2023
In India, the informal sector represents a significant portion of the workforce, employing more than 90% of workers and contributing
- December 2, 2020
- September 20, 2020
- August 20, 2020